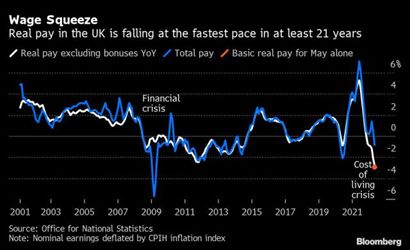
Earnings growth increased across the private and public sector by 4.3% in the three months to May excluding bonuses, the ONS said, but that left pay down by record 3.7%
British workers’ living standards dropped in May at a record rate after pay rises failed to keep pace with inflation.
Earnings growth increased across the private and public sector by 4.3% in the three months to May excluding bonuses, the Office for National Statistics said, but that left pay down by 3.7% – a record fall.
Labour blamed the Conservative government for the fall in real wages, saying it ‘left people more exposed to inflation and the cost of living crisis’.
The TUC general secretary, Frances O’Grady, said candidates in the Conservative party leadership election should be mindful that ‘UK workers are suffering the worst pay squeeze in modern history’.
She added: The priority for the country must be to get wages rising across the economy – not tax cuts.
Public sector workers fared much worse than those in the private sector, where pay growth was nearly five times faster. Average pay growth including bonuses for the private sector was 7.2% in the three months from March to May, while for the public sector it was 1.5%, leaving an average of 6.2%.
The government is expected to announce pay awards for 2.5 million public sector workers on Tuesday, with reports that it will offer average pay rises of 5%. That would be well below the 9.1% rate in inflation, which is heading above 11% in the autumn according to the Bank of England.
Strong bonus payments in some sectors gave a boost to the figures, the ONS said, with pay in the financial and professional services and construction sectors growing by 8.2% and 8.1%, respectively.
The ONS said the 4.3% increase in pay without bonuses marked a 2.8% fall in earnings against its preferred measure of inflation – the consumer prices index including housing (CPIH). Against the standard CPI measure of inflation used by the Treasury and Bank of England, the drop in real pay over the three months to May was 3.7%, the TUC said.
There was better news from figures showing the number of people in employment jumped in May. More than 290,000 workers joined the labour market, about 120,000 more than forecast by City analysts. Meanwhile, unemployment remained steady at 3.8% and employers pushed up the level of vacancies to a fresh high.
But employers failed to attract many of the workers who quit the labour market during the pandemic to leave the employment rate of 75.9% below pre-pandemic levels.
Business groups complained that firms struggled to recruit staff, causing delays to orders and a loss of income.
Jane Gratton, a senior official at the British Chamber of Commerce, said: The labour market remains incredibly tight, in many cases affecting firms’ ability to maintain normal operations. Although these figures show the employment rate has risen, it is having no noticeable impact on the overall number of job vacancies.
She added that an acute shortage of workers was ‘choking off any hope of a recovery for many firms; as inflation, supply chain disruption and energy costs also add to their headaches’.
Matthew Percival, a spokesperson for the CBI, said: Persistent labour and skills shortages are hitting growth and business investment, exacerbating the cost-of-living crisis. Boosting business confidence to accelerate growth should be front of mind for the current and next government.
Bank of England officials are expected to raise interest rates when they meet next month despite warnings of an impending recession and pay increases falling short of inflation.
Analysts said the Bank’s monetary policy committee (MPC) would focus on the tightness of the labour market after a much larger than expected increase in employment and how this could translate into higher pay rises as the year progresses.
Many of the MPC’s nine members fear that without higher interest rates to slow the economy, workers will drive wages towards the current 9.1% level of inflation, adding to business costs and pushing prices higher next year.







Leave a Reply